Developing a Program of All-inclusive Care for the Elderly (PACE) program requires a significant capital investment, an appetite for risk, and access to a robust network of health care providers and services. Some organizations are able to develop a PACE program as a sole sponsor, but for many organizations, it may be necessary to explore partnerships with a second or even multiple organizations to responsibly develop and operate a PACE program.
This post will explore the various types of organizations that sponsor PACE, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of a partnership.
Sponsorship by Organization Type
PACE centers on the belief that it is better for the well-being of seniors with chronic care needs, and their families, to be served in the community whenever possible. By providing or coordinating all needed medical and supportive services through an interdisciplinary team (IDT), PACE programs are able to provide the entire continuum of care and services to older adults with chronic care needs, while enabling them to maintain independence in their homes for as long as possible.
There are many different types of organizations that are PACE sponsors. Sponsors typically include senior services organizations or organizations that work with seniors in some capacity.
Figure 1 shows the current distribution of PACE sponsors.
Figure 1: PACE Sponsorship by Organization Type
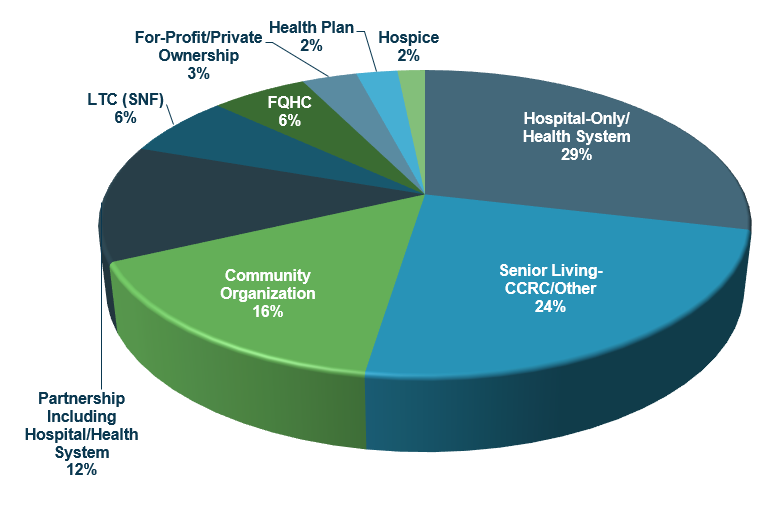 Source: National PACE Association
Source: National PACE Association
As shown on Figure 1, hospitals/health systems are the most common type of PACE sponsor, as either the sole sponsor or as part of a partnership. Other providers include: senior living, community organizations, long-term care (LTC) facilities, Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs), private ownership, health plans, and hospice organizations.
What all sponsors have in common is the desire to provide quality care for seniors. PACE may provide an alternative option to the sponsor’s other services, fill a void in the market, or be used to manage population health.
In addition to hospitals and health systems, among the faster growing sponsor organizations are FQHCs and partnerships.
PACE Partnership: The Advantages
Partnerships are becoming more common, particularly due to the increasing cost of starting a PACE program. Advantages of partnership include sharing the downside risk that comes with operating PACE and combining the resources critical to development and operation. These resources may include:
- Capital
- Building to be used as the PACE center
- Services critical to PACE, such as home care or a network of specialty physicians
- Management or back office capabilities
- Referral sources
- Access to potential enrollees
PACE Partnership: The Disadvantages
Not all partnerships that begin the process of exploring PACE together come to fruition. Notable disadvantages of a PACE partnership include a lack of control over decision-making and profits. More than one sponsor means more than one decision-maker and distribution of earnings. Although both sponsors may be exploring PACE for the right reasons, their reasons may not always align.
Asking the Right Questions When Exploring a PACE Partnership
There are many things to consider when exploring a partnership. These decisions often take many months to negotiate, so be patient. Below is a partial list of things to consider:
- Is there mission alignment between the organizations?
- Is PACE a good fit for each organization and is each organization a good fit for PACE?
- Is each organization able to contribute value to the PACE program?
- Is this a planned short-term or long-term partnership?
- Is there agreement on decision-making authority and profit distribution?
- How will the PACE sponsoring organization be structured?
- How will start-up capital be funded?
- How will PACE operations be structured?
- Is there mutual respect and an open line of communication for resolution of disagreements?
- Is there sustained leadership support from all parties?
- Are all organizations comfortable with risk?
- What are competing priorities that may delay or derail the process?
As shown above, there are many questions that need to be explored when forming a partnership. PACE organizations have been successful with multiple sponsors, but as with any partnership, careful planning must be completed or the program may fall short of maximum potential due to sponsor distractions.
Is My Organization a Good Fit to Sponsor PACE?
As a National PACE Association Technical Assistance Center, Health Dimensions Group (HDG) has successfully assisted many organizations with PACE market and financial feasibility studies, program development and implementation support, and operational improvement. If you would like to learn more about how HDG can assist you in exploring PACE as a solution in today’s challenging health care environment, please contact us at 763.537.5700 or info@hdgi1.com and visit our website.












